Diabetes is one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide.
The longer a person suffers from diabetes, the greater the chance he or she has for developing diabetic eye disease. In fact, 80% of patients who have diabetes will develop eye problems after 10 or more years.
Unfortunately, up to 50% of diabetics remain undiagnosed and untreated, and about 30% of patients already have their eyes affected by the time they are first diagnosed with diabetes.
The current international guidelines recommend an eye exam at least once a year for every diabetic patient to screen for diabetic retinopathy since treatments are most effective when used early.
At American Eye Center Vietnam, we can prevent up to 90% of cases of blindness by following the latest American and international treatment protocols for diabetic retinopathy with medications, injections, laser surgery, and vitrectomy surgery..
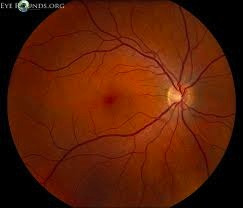
If you have diabetes mellitus, your body does not use and store glucose properly. Over time, diabetes can damage blood vessels in the retina, the nerve layer at the back of the eye that senses light and helps to send images to the brain. The damage to retinal vessels is referred to as diabetic retinopathy.
 |
 |
| Normal retina | Diabetic Retinopathy |
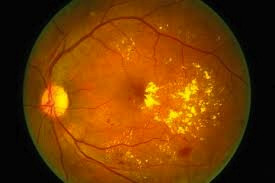
This is an early stage of diabetic retinopathy. In this stage, tiny blood vessels within the retina leak blood or fluid.
The leaking fluid causes the retina to swell or to form deposits called exudates.
This is swelling or thickening of the macula, a small area in the center of the retina that allows us to see fine details clearly.
The swelling is caused by fluid leaking from retinal blood vessels. It is the most common cause of visual loss in diabetes.
Occurs in advanced diabetes, where the retinal blood vessels are so damaged they close off.
In response, the retina grows new, fragile blood vessels. Unfortunately, these abnormal new blood vessels do not function well to carry oxygen to the retina.
Occurs when the new abnormal blood vessels rupture and bleed into the cavity of the eye.
A small amount of blood will cause dark floaters, while a large hemorrhage might block all vision, leaving only light and dark perception.
The new blood vessels can also cause scar tissue to grow. The scar tissue shrinks, wrinkling and pulling on the retina and distorting vision.
If the pulling is severe, it may cause a retinal detachment and cause vision loss.
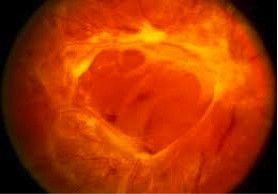
Retinal detachment
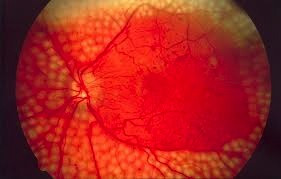
Currently there are many treatments to restore vision and prevent worsening of the disease. Macular edema and new blood vessels can be treated with eye injections and laser surgery. If there is vitreous hemorrhage lasting more than 6 months, or if a retinal detachment is detected, an operation called a vitrectomy can be performed.
During a vitrectomy, the eye surgeon removes the hemorrhage and any scar tissue that has developed, and performs laser treatment to prevent new abnormal vessel growth.
 |
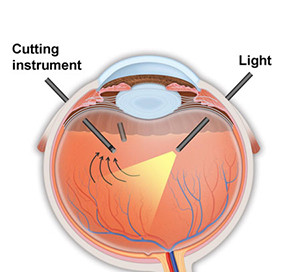 |
| Laser Treatment | Vitrectomy Surgery |
Phone: 0938 136 758
Address: Golden House, 90 Nguyen Huu Canh, Ward 22, Binh Thanh District, HCMC
Get DirectionsEmail: web@americaneyecentervn.com
Hotline: 0938 136 758
Website: americaneyecenter.com